Research Express | Tsinghua University study shows NMN can treat inflammation
- Categories:Industry News
- Time of issue:2022-09-27 14:15
- Views:
(Summary description)Hypopigmentation is a skin disease, mainly manifested by melanin reduction. Common symptoms include vitiligo, albinism and hypopigmentation after skin inflammation. At present, the main treatment for hypopigmentation is oral medicine, but oral medicine will cause skin atrophy, gastrointestinal discomfort and other adverse side effects. Therefore, it is necessary to develop a natural substance without side effects to treat hypopigmentation.
Research Express | Tsinghua University study shows NMN can treat inflammation
- Categories:Industry News
- Time of issue:2022-09-27 14:15
- Views:
Macrophage activation is a pathogenic mechanism leading to chronic inflammation in the body , but persistent macrophage activation can lead to chronic inflammation and diseases such as insulin resistance and severe diseases such as atherosclerosis. PGE 2 , which mediates the inflammatory response, is synthesized from arachidonic acid by cyclooxygenases (COX-1 and COX-2) . COX-1 and COX-2 are the main targets of anti-inflammatory and can be inhibited by non- steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) .
use of NSAIDs can cause many adverse reactions , such as gastrointestinal bleeding . Therefore, it is particularly important to find a safer natural substance to treat inflammation .

Recently, a research team from Tsinghua University treated mouse macrophages with NMN, and proved through experiments that NMN can reduce the accumulation of inflammation-related proteins and metabolic byproducts, and inhibit the inflammatory response of macrophages . Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences .
Inflammation alters levels of metabolic byproducts in macrophages
First, the research team activated macrophages to produce inflammation through lipopolysaccharide (LPS ) , and then analyzed the content of byproducts around macrophages during inflammation . The levels of 99 metabolites were increased and 105 metabolites were decreased among the 458 molecules detected before and after inflammatory stimulation , and NAD+ levels that accompany inflammation were also decreased.
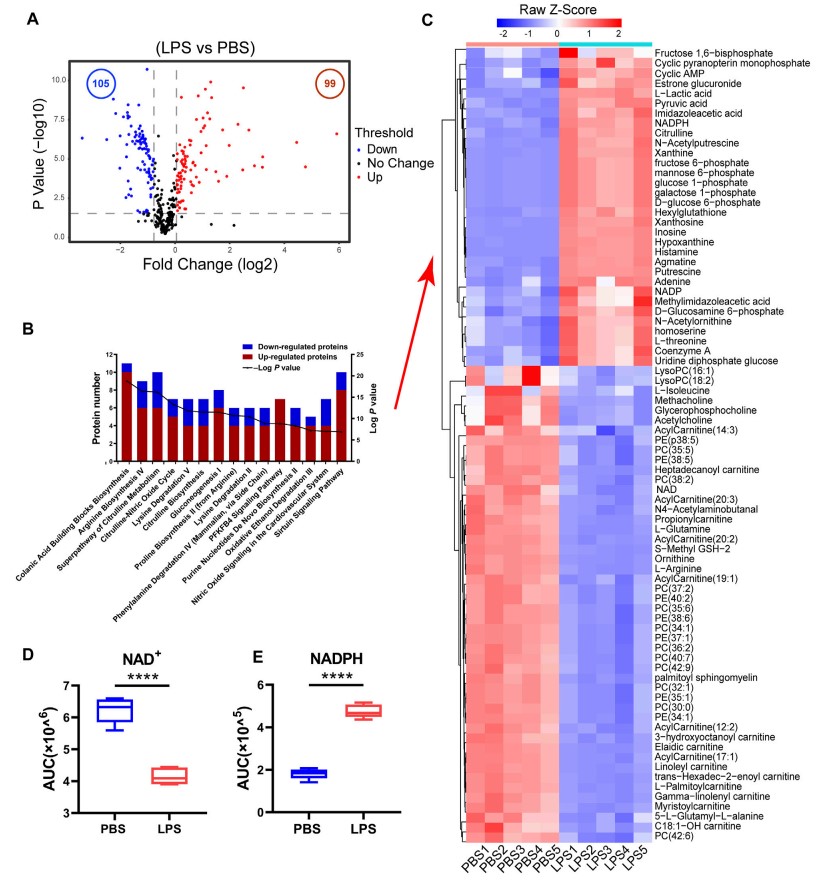
(FIGURE 1)
NMN increases NAD levels and reduces macrophage inflammation
The research team then treated macrophages with LPS, which induces an inflammatory state, IL-6 and IL-1β, pro-inflammatory cytokines that act as markers of inflammation . After NMN treatment of LPS-induced macrophage inflammation , it was found that the intracellular NAD level was increased and the mRNA expression of IL-6 and IL-1β was decreased . Experiments demonstrated that NMN increased the level of NAD and attenuated LPS-induced macrophage inflammation .

( Figure 2 )
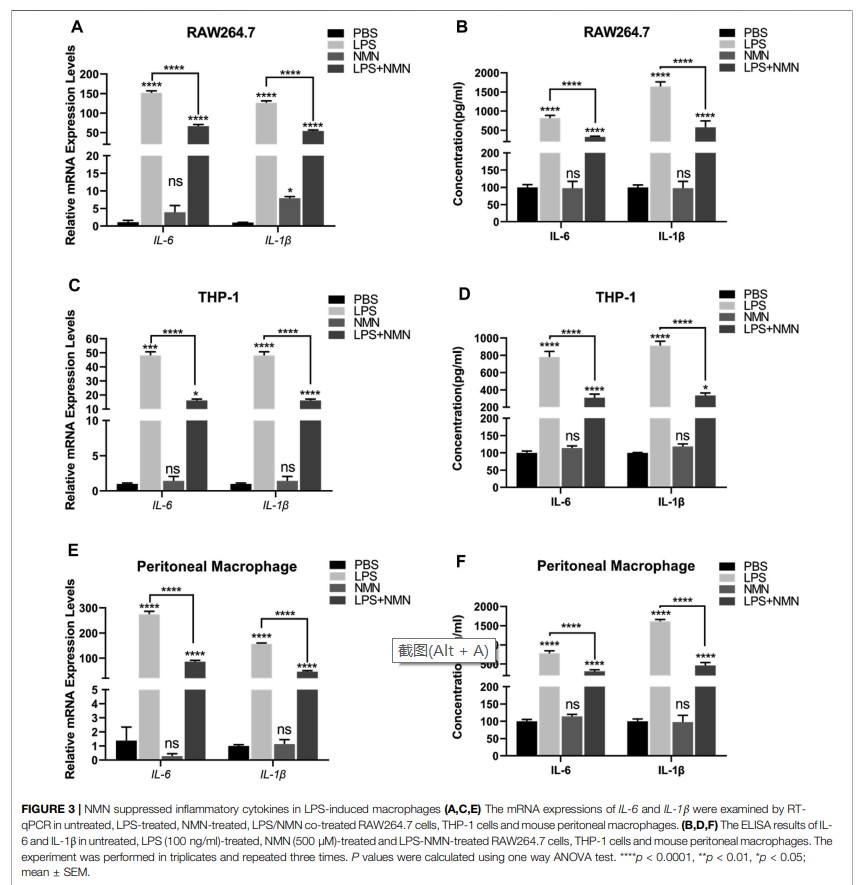
( Figure 3 )
NMN reduces inflammation-related protein levels
NMN treatment, it was found that proteins related to inflammation such as RELL1 , PTGS2, FGA, FGB and igkv12-44 were decreased in cells , which indicated that NMN reduced the expression of inflammation-related proteins .

( Figure 4 )
NMN reduces the expression of NSAIDS target proteins
The final experiment found that NMN reduced the level of PGE2 in LPS-activated RAW264.7 cells by reducing the expression level of COX-2 , thereby reducing the expression of COX2 and inhibiting LPS-induced inflammation.

( Figure 6 )
conclusion , supplementation of NMN can effectively treat chronic inflammation in mice, and the treatment of inflammation in humans still needs to be verified by relevant clinical trials. Perhaps NMN will become a substitute for NSAIDS in the near future.
references:
1.Liu J, Zong Z, Zhang W, Chen Y, Wang X, Shen J, Yang C, Liu X, Deng H. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Alleviates LPS-Induced Inflammation and Oxidative Stress via Decreasing COX-2 Expression in Macrophages. Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Jul 6.
Search

Tel:021-68187180
Fax:021-68187179
E-mail:services@syncozymes.com
Address: No. 1199, Landian Road, Zhoupu Town, Pudong New Area, Shanghai

Copyright ©SyncoZymes (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. 沪ICP备09012407号 By:300.cn
-
-
-
Customer service contact information
Service hours:9:00-18:00
Contact number:
I want to leave a message:
-

