New research in Europe: NMN can improve the antiviral activity of CD8 T cells, a specific immune cell of patients with hepatitis B.
- Categories:Industry News
- Time of issue:2023-05-19 13:52
- Views:
(Summary description)For patients with chronic hepatitis B, the high level exposure of hepatitis B virus-specific immune cells (CD8 T cells) to pathogens such as hepatitis B virus has caused DNA damage and dysfunction of CD8 T cells. Identifying the cellular process behind CD8 T cell damage is helpful to develop the treatment of chronic hepatitis B.. Recent studies have shown that NAD+ depletion is the basis of CD8 T cell depletion.
New research in Europe: NMN can improve the antiviral activity of CD8 T cells, a specific immune cell of patients with hepatitis B.
- Categories:Industry News
- Time of issue:2023-05-19 13:52
- Views:
For patients with chronic hepatitis B, the high level exposure of hepatitis B virus-specific immune cells (CD8 T cells) to pathogens such as hepatitis B virus has caused DNA damage and dysfunction of CD8 T cells. Identifying the cellular process behind CD8 T cell damage is helpful to develop the treatment of chronic hepatitis B.. Recent studies have shown that NAD+ depletion is the basis of CD8 T cell depletion.
Recently, a team of Professor Fisicar from the University of Parma, Italy, published an article entitled "Defined intrinsic pathways for HBV-specific CD8 t cell reconstruction in chronic hepatitis B." in Journal of Hepatology.
This article provides evidence for the role of NMN in the treatment of hepatitis B, and shows that NMN can be used to repair the damaged CD8 T cells to resist chronic hepatitis B virus.
The researchers first isolated immune cells from patients with chronic hepatitis B, and then treated them with NMN, and found that the immune cells expressed more antiviral cytokines, especially the cytokine interferon-γ (IFN-) increased by 2.7 times. The results showed that NMN restored the antiviral characteristics of CD8 T cells.
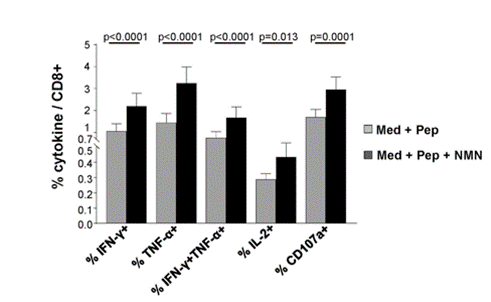
Figure | NMN can restore the production of antiviral cytokines in immune cells.
In order to prove that chronic hepatitis B infection will be accompanied by CD8 T cell damage, the researchers compared the DNA damage of CD8 T cells and flu-specific T cells in patients with hepatitis B.. Researchers found more DNA damage in CD8 T cells of hepatitis B.. They also found that compared with FLU-specific T cells, treating cells with DNA damage-inducing molecules (etoposide) would lead to a decrease in DNA damage response. Because PARP-mediated DNA damage requires NAD+, this data indicates that NAD+ deficiency is related to a higher level of DNA damage in hepatitis B-specific CD8 T cell failure.
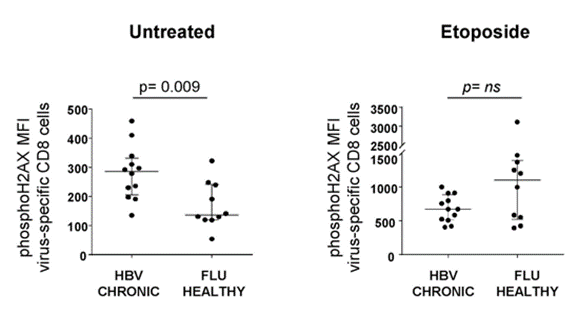
Figure | CD8 T cells in hepatitis B have a high level of DNA damage.
In order to further explore how NAD+ supplementation with NMN can improve the production of antiviral cytokines in damaged CD8 T cells, the researchers examined the relationship between the high level of CD38 enzyme consuming NAD+ and the level of cytokines. They measured IFN-, a major cytokine, and found that high CD38 enzyme level was associated with low IFN-level. These data provide evidence that high CD38 enzyme levels can lead to a decrease in antiviral cytokine production. This also makes the inference that low NAD+ level plays an important role in the pathology of chronic hepatitis B credible, because high CD38 level will theoretically reduce NAD+ in cells.
The experimental results show that nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) can effectively enhance the antiviral activity of CD8 T cells, the specific immune cells of patients with chronic hepatitis B, thus improving their antiviral ability. This provides a potential strategy for further research and exploration of immunotherapy.
Literature source:
Montali I, Berti CC, Morselli M, Acerbi G, Barili V, Pedrazzi G, Montanini B, Boni C, Alfieri A, Pesci M, Loglio A, Degasperi E, Borghi M, Perbellini R, Penna A, Laccabue D, Rossi M, Vecchi A, Tiezzi C, Reverberi V, Boarini C, Abbati G, Massari M, Lampertico P, Missale G, Ferrari C, Fisicaro P. Deregulated intracellular pathways define novel molecular targets for HBV-specific CD8 T cell reconstitution in chronic hepatitis B. J Hep atol. 2023 Mar 7:S0168-8278(23)00167-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.02.035. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 36893853.
Search

Tel:021-68187180
Fax:021-68187179
E-mail:services@syncozymes.com
Address: No. 1199, Landian Road, Zhoupu Town, Pudong New Area, Shanghai

Copyright ©SyncoZymes (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. 沪ICP备09012407号 By:300.cn
-
-
-
Customer service contact information
Service hours:9:00-18:00
Contact number:
I want to leave a message:
-

